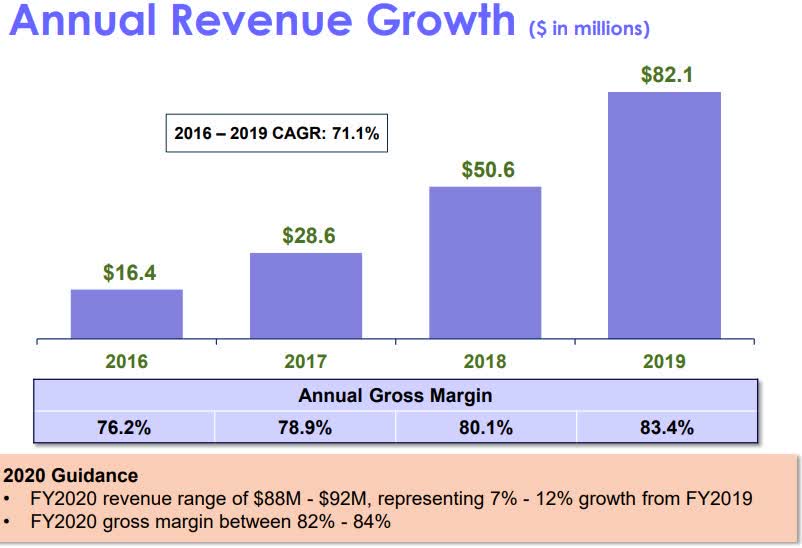
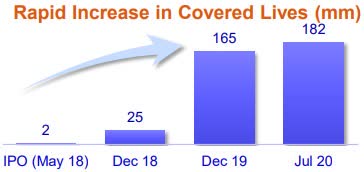
Results from a 39-patient case-control study in hospitalized COVID-19 patients showed a significant treatment benefit from Humanigen’s (
OTCQB:HGEN) lenzilumab, its Humaneered anti-human granulocyte macrophage-colony stimulating factor (GM-CSF) monoclonal antibody. The data were just published in
Mayo Clinic Proceedings.
12 severely ill patients received lenzilumab and 27 contemporaneous matched control patients, identified from an electronic registry of COVID-19 patients matched for age, sex, disease severity and baseline oxygen requirements, received standard-of-care (SOC) treatment.
The relative risk of invasive mechanical ventilation (IMV) and/or death was reduced 80% in the lenzilumab group. Specifically, the risk of IMV and/or death was 8% in lenzilumab-treated patients compared to 41% in the control group (p=0.07).
Median time to resolution of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) was one day in lenzilumab patients versus eight days in the control group (p<0.01). Median time to discharge was shorter in the lenzilumab group, five days versus 11 days (p=0.008).
Lenzilumab was also associated with a significant reduction in an inflammatory marker called c-reactive protein and improved lymphocyte counts.
The antibody is currently being evaluated in a Phase 3 NIH study called COVID-19 Big Effect.