Researchers have generated six Zika virus antibodies that could be used to test for and possibly treat a mosquito-borne disease that has infected more than 1.5 million people worldwide.
The antibodies “may have the dual utility as diagnostics capable of recognizing Zika virus subtypes and may be further developed to treat Zika virus infection,” corresponding author Ravi Durvasula, MD, and colleagues report in a study published in the journal PLOS ONE.
Dr. Durvasula is professor and chair of the department of medicine of Loyola Medicine and Loyola University Chicago Stritch School of Medicine. First author is Adinarayana Kunamneni, PhD, a research assistant professor in Loyola’s department of medicine.
Zika is spread mainly by mosquitos. Most infected people experience no symptoms or mild symptoms such as a rash, mild fever and red eyes. But infection during pregnancy can cause miscarriages, stillbirths and severe birth defects such as microcephaly.
Zika virus is a textbook example of an emerging disease that appears quickly, often in remote areas with little or no public health infrastructure. There is no effective vaccine or drug to treat the disease.
“The recent Zika virus outbreak is a health crisis with global repercussions,” Drs. Durvasula, Kunamneni and colleagues write in the PLOS ONE study. “Rapid spread of the disease within the epidemic regions, coupled with migration of infected persons, has underscored the need for rapid, robust and inexpensive diagnostic tools and therapeutics.”
Antibodies could be key to diagnosing and treating Zika virus. An antibody is a Y-shaped protein made by the immune system. When a virus, bacterium or other pathogen invades the body, antibodies bind to antigens associated with the bug, marking it for the immune system to destroy.
Using a technology called ribosome display, researchers generated six synthetic antibodies that bind to the Zika virus. The antibodies, which are inexpensive to produce, could be used in a simple filter paper test to detect the Zika virus in the field. (If the filter paper turns color, the Zika virus is present.)
Because the Zika virus is evolving, it’s useful to have six different antibodies. In the event the virus mutates, it’s likely at least one of the antibodies still would match the virus and thus could still be used in diagnosis and treatment.
An antibody-based test for the Zika virus likely would be cheap and fast, and thus could easily be used to monitor mosquito populations for Zika. If the virus is present in an area, officials could respond by stepping up mosquito-abatement efforts. They also could educate the public — especially women who are pregnant or could become pregnant — on how to avoid mosquito bites by applying mosquito repellent, wearing long pants and long-sleeve shirts, eliminating standing water, etc.
The antibodies are “neutralizing,” meaning that when they bind to the Zika virus, they prevent the virus from infecting cells. This effectively renders the virus harmless. The neutralizing property potentially could lead to the development of a drug that an at-risk woman could take to prevent the virus from infecting her fetus.
It will take further research to validate the antibodies’ potential for diagnosing and treating Zika virus, researchers said.
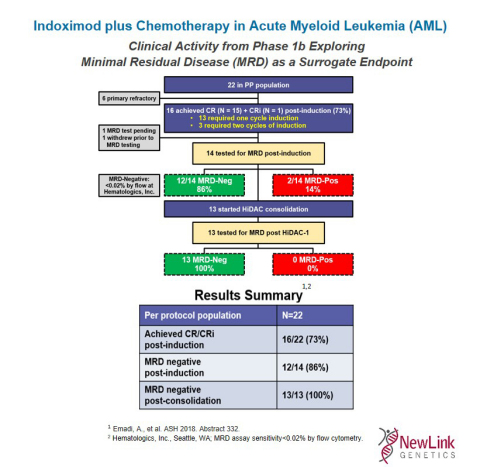 Indoximod plus Chemotherapy in Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) (Graphic: Business Wire)
Indoximod plus Chemotherapy in Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) (Graphic: Business Wire)